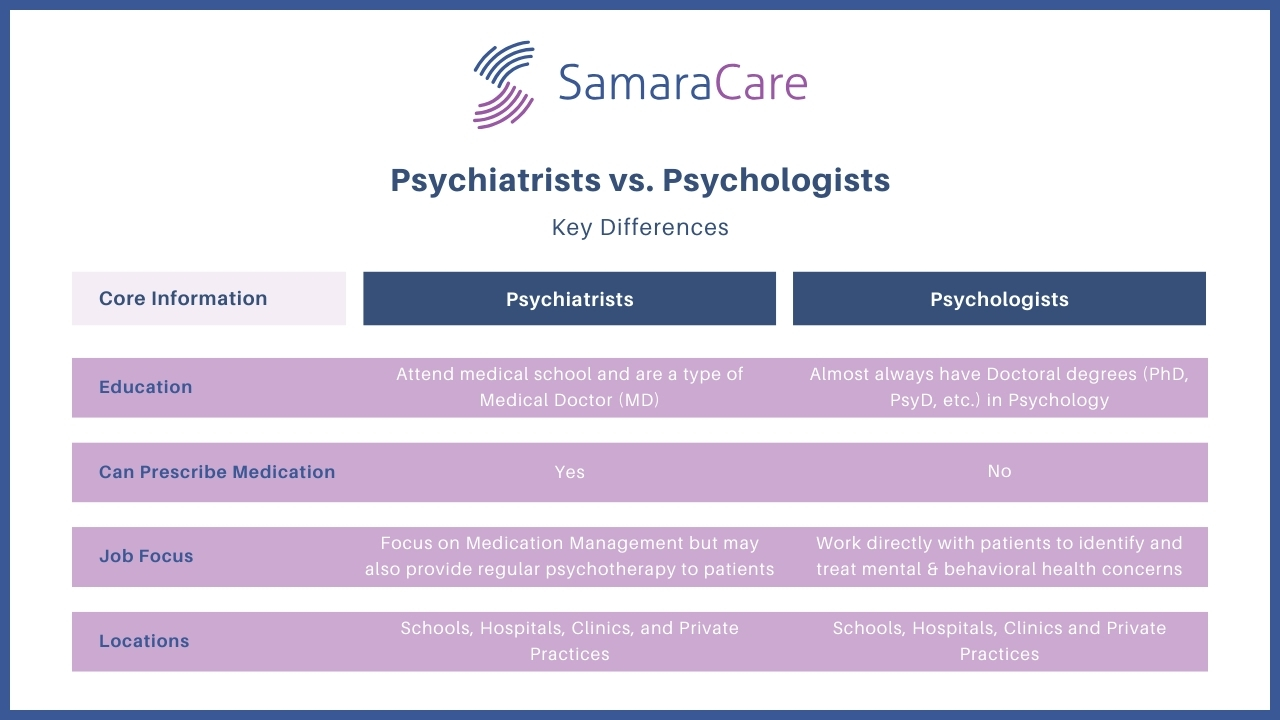
Mental health professionals play vital roles in supporting emotional and psychological well-being, but distinguishing between psychiatrists and psychologists can be confusing. The primary difference is that psychiatrists are medical doctors who can prescribe medication, while psychologists focus on therapy, psychological testing, and behavioral interventions. Today we’ll answer a common question: What’s The Difference Between Psychiatric and Psychological?
Psychiatrists complete medical school and residency, giving them expertise in biological aspects of mental health conditions. In contrast, psychologists typically hold doctoral (PhD or PsyD) or Master’s degrees specializing in human behavior, emotional processes, and therapeutic techniques. In both instances they are licensed professionals.
Your treatment needs will help determine which professional to consult. When you need medication management for conditions like depression or anxiety, a psychiatrist can help. For talk therapy (psychotherapy) and psychological assessment, working with a psychologist or counselor may be more appropriate.
Key Takeaways
- Psychiatrists can prescribe medications while psychologists focus on therapeutic interventions.
- Both professionals require extensive education but follow different training paths.
- Modern mental health care often involves collaboration between psychiatrists, psychologists and counselors.
Defining the Fields: Psychology and Psychiatry
Mental health care encompasses two distinct disciplines that approach treatment and care from different angles, with unique methods and qualifications. Each field requires specific educational paths and offers different types of interventions for mental health concerns. Today you’ll learn the difference between a psychologist and a psychiatrist!
Psychiatry Overview
Psychiatrists are medical doctors who specialize in diagnosing and treating mental health conditions through medical interventions. They complete medical school followed by a psychiatric residency.
Your psychiatrist can prescribe medications and order laboratory tests to evaluate your physical and mental health conditions. They focus on the biological aspects of mental health, including brain chemistry and neurological functions.
Psychiatrists often work in hospitals, private practices, non-profits, or mental health clinics. They regularly monitor medication effects and make adjustments to your treatment plan based on your body’s response.
Psychology Overview
Psychologists focus on behavior, emotions, and thought patterns through various therapeutic techniques. When seeking a career in psychology, they work towards holding a doctoral psychology degree (Ph.D. or Psy.D.), or a Master’s level degree rather than medical degrees.
Your psychologist or counselor uses various therapeutic modalities to help you understand and modify your behaviors and thought patterns. They specialize in psychological testing and assessment to evaluate mental health conditions and cognitive functions.
Psychologists and counselors work in diverse settings, including private practices, schools, research facilities, non-profits, and corporations. They help you develop coping strategies and behavioral changes through regular therapy sessions.
Professional Services at SamaraCare
SamaraCare offers a dedicated team of in-house mental health professionals, including psychiatrists, psychologists, social workers, and a Psychiatric Nurse Practitioner, ensuring seamless collaboration for comprehensive care. With 7 psychiatrists and a skilled group of psychologists, most of our counselors are experienced social workers or LCPCs, providing expert support for your mental well-being.
Educational Background

Educational paths for mental health professionals differ significantly in length, focus, and requirements. Each path leads to distinct qualifications and capabilities in treating mental health conditions.
Psychiatrist Education
To become a psychiatrist, you must complete medical school after earning a bachelor’s degree. The medical doctor (MD) training takes 4 years, followed by a 4-year residency in psychiatry.
During medical school, you’ll study anatomy, biology, pharmacology, and general medical practice. This foundation enables you to understand the physical aspects of mental health conditions.
Psychiatric residency programs focus on diagnosing mental illnesses, prescribing medications, and managing complex cases. You’ll work directly with patients under supervision while learning specialized treatment approaches.
Psychologist Education
As a psychologist, you’ll need to earn a doctoral degree – either a PhD (Doctor of Philosophy) or PsyD (Doctor of Psychology). Doctoral programs typically focus on behavioral science, research methods, and therapeutic techniques.
Your education begins with a bachelor’s degree, followed by 5-7 years of graduate study. PhD programs emphasize research and academic work, while PsyD programs focus more on clinical practice.
Clinical training includes supervised practicum experiences and a one-year internship. You’ll learn various therapy techniques, psychological testing methods, and treatment planning strategies.
Most states require additional post-doctoral supervised experience before you can become licensed to practice independently.
Areas of Practice

Mental health professionals work in distinct specialties with specific approaches to diagnosis and treatment. Each field requires unique expertise and serves different patient needs through specialized methods and tools.
Clinical Psychiatry
Psychiatrists focus on diagnosing and treating mental illnesses through medical interventions. They can prescribe medications and monitor biological treatments.
Your psychiatrist will evaluate your symptoms through a medical lens, considering how brain chemistry and physical health affect your mental well-being. They often work in hospitals, private practices, non-profits, and mental health facilities.
Common psychiatric treatments include:
- Antidepressant medications
- Mood stabilizers
- Antipsychotic drugs
- Electroconvulsive therapy
- Psychotherapy combined with medication
Clinical Psychology
Psychologists specialize in behavioral assessment and therapeutic interventions. They use various therapy techniques to help you understand and modify your thoughts and behaviors.
Your psychologist will conduct psychological testing and assessments to evaluate your mental processes and behavior patterns. They typically work in private practices, clinics, non-profits, and counseling centers.
Key psychological services include:
- Cognitive behavioral therapy
- Individual and group counseling
- Psychological testing
- Behavior modification
- Family therapy
Research and Academic Perspectives
In research settings, both fields contribute to advancing mental health knowledge. Modern treatment approaches often integrate both psychological and psychiatric perspectives.
You’ll find psychiatrists conducting clinical trials on new medications and treatment methods. Their research often focuses on biological factors in mental illness.
Psychologists typically research human behavior, cognitive processes, and therapeutic techniques. They develop and test new psychological interventions and assessment tools.
Both professions contribute to the academic training of new practitioners and publish findings in scientific journals.
Treatment Approaches

Psychiatric and psychological professionals use distinct therapeutic methods based on their training and expertise. Your treatment plan may include medication, therapy, or a combination of both depending on your specific needs.
Medication and Biological Treatments
Medication and biological treatments are vital components in the treatment of mental health disorders. The field of psychology primarily addresses the therapeutic aspects, while psychiatry focuses on medical interventions. A licensed psychologist holds a degree in psychology and is trained to work with patients through various therapeutic techniques. In contrast, a psychiatrist, who typically must attend medical school, can prescribe medications to treat mental health issues. The differences between the two professions are significant; while both aim to improve the lives of those with mental disorders, their approaches differ greatly.
Psychiatrists can prescribe medications to help manage your mental health symptoms. These medications might include antidepressants, antianxiety drugs, or antipsychotics.
Your psychiatrist will monitor your response to medication and adjust dosages as needed. They may also recommend other biological treatments.
Regular check-ups help ensure your medication remains effective and properly manages any side effects.
Becoming a psychologist typically involves obtaining a doctoral degree in psychology, which prepares individuals for various career paths in the field. Furthermore, a clinical psychologist specializes in assessing and treating mental health disorders through therapy. Conversely, addiction psychiatry is a branch of psychiatry that specifically deals with substance misuse disorders.
Psychotherapy and Behavioral Interventions
Psychologists focus on therapeutic techniques to help you understand and change thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. Common approaches include cognitive-behavioral therapy, psychodynamic therapy, and behavioral interventions.
Your psychologist or counselor will work with you to develop coping strategies and problem-solving skills. These sessions typically involve regular conversations and structured exercises.
Treatment length varies based on your needs – some people benefit from short-term therapy lasting a few months, while others may need longer-term support.
You might learn specific techniques like:
- Stress management skills
- Mindfulness practices
- Communication strategies
- Behavioral modification tools
Professional Settings: Mental Health Locations
Mental health professionals work across diverse environments to serve different patient populations and organizational needs. Their specialized training and expertise determine where they can practice most effectively.
Private Practice and Hospitals
Psychiatrists as medical doctors work in hospitals, clinics, non-profits, and private practices where they can prescribe medications and provide comprehensive medical care.
Treatment allows psychiatrists, psychologists, and counselors to develop long-term therapeutic relationships when appropriate.
In hospital settings, psychiatrists often handle acute cases requiring immediate medical intervention and work closely with other healthcare providers.
Schools and Industrial-Organizational Roles
Psychologists have unique opportunities in educational institutions, where they conduct assessments, provide counseling, and support student development.
In corporate settings, industrial-organizational psychologists apply psychological principles to workplace dynamics, employee performance, and organizational culture.
Your school psychologist might help with learning assessments and behavioral interventions, while workplace psychologists focus on team dynamics and employee well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions: What’s The Difference Between Psychiatric and Psychological

Mental health professionals serve distinct but complementary roles in treating psychological and psychiatric conditions, with different approaches to assessment, treatment methods, and professional qualifications.
Should I consult a psychologist or psychiatrist for depression?
Both mental health professionals can help treat depression, but their approaches differ. A psychiatrist can prescribe antidepressant medications and monitor their effects on your symptoms.
A psychologist focuses on therapy and counseling to help you develop coping strategies and address underlying thought patterns. Many people benefit from working with both providers simultaneously.
What is the main difference between a psychologist and a psychiatrist?
The primary difference between a psychologist and a psychiatrist lies in their educational background and approach to mental health treatment. Psychiatrists are medical doctors who have completed medical school and specialized in psychiatry. They can prescribe medication and are trained to diagnose and treat mental health disorders from a medical perspective. Psychologists, on the other hand, have a degree in psychology and focus on psychotherapy and behavioral interventions. While both psychiatrists and psychologists can diagnose and treat mental health issues, their methods and areas of expertise may differ.
When seeking help for anxiety, should one prefer a psychologist or psychiatrist?
Your choice depends on your symptoms and preferences. A psychiatrist might be appropriate if you’re interested in medication management for severe anxiety symptoms.
A psychologist can teach you anxiety management techniques and help identify triggers through therapy. Many anxiety patients work with both providers for comprehensive care.
SamaraCare offers treatment from both in-house psychiatrists and psychologists.
Can a psychologist prescribe medication?
In most cases, psychologists cannot prescribe medication. This is one of the key differences between psychology and psychiatry. Psychiatrists, being medical doctors, have the authority to prescribe medication for mental health disorders. However, there are a few exceptions. In some states in the United States, psychologists with additional training in psychopharmacology may be granted limited prescribing rights. But generally, if medication is needed as part of treatment, a psychologist will refer the patient to a psychiatrist or other medical doctor. A Psychiatric Nurse Practitioner may also be authorized to prescribe medication. SamaraCare has a full-authority, experienced Psychiatric Nurse Practitioner.
What distinguishes a psychological disorder from a psychiatric disorder?
Psychological disorders typically involve behavioral and emotional patterns that affect daily functioning and relationships. These often respond well to therapy and behavioral interventions.
Psychiatric disorders frequently have biological components that may require medication management alongside therapeutic approaches.
In what ways do psychological assessments differ from psychiatric assessments?
Psychological assessments include detailed personality tests, cognitive evaluations, and behavioral observations to understand thinking patterns and behaviors.
Psychiatric assessments focus more on medical history, symptoms, and biological factors to determine medication needs and diagnose specific mental health conditions.
What are the different functions of a psychologist, psychiatrist, and psychotherapist?
Psychiatrists are medical doctors who can prescribe medication and treat mental health conditions from a medical perspective.
Psychologists specialize in therapeutic techniques and psychological testing. They help patients through various forms of talk therapy and behavioral interventions.
Psychotherapists may come from either background and focus primarily on providing therapy services. Their specific approach depends on their training and credentials.
What kind of education, training, and career paths do psychiatrists undergo?
Psychiatrists undergo extensive education and training to become specialists in mental health. They first complete a bachelor’s degree, followed by four years of medical school to become a medical doctor. After medical school, they complete a four-year residency in psychiatry, where they gain hands-on experience in diagnosing and treating a wide range of mental health disorders. During their residency, they work in various settings, including hospitals, outpatient clinics, and community mental health centers, allowing them to develop a comprehensive understanding of different psychiatric conditions and treatment modalities.
In addition to their clinical training, psychiatrists learn about psychopharmacology, psychotherapy, and the biological, psychological, and social factors that contribute to mental health issues. They also engage in research and may have the opportunity to teach medical students or supervise residents as they advance in their careers.
After completing their residency, many psychiatrists choose to pursue board certification by passing an examination administered by the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology. All psychiatrists at SamaraCare are board-certified. Some may also opt for further specialization in areas such as child and adolescent psychiatry, geriatric psychiatry, addiction psychiatry, or forensic psychiatry, which often requires additional fellowship training.
Throughout their careers, psychiatrists must stay current with advancements in the field by participating in continuing medical education (CME) and keeping up with the latest research and treatment guidelines. This dedication to lifelong learning ensures that they can provide the best possible care to their patients and adapt to the evolving landscape of mental health treatment.
In their practice, psychiatrists often collaborate with other healthcare professionals, such as psychologists, social workers, and primary care physicians, to create a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to the individual needs of their patients. They utilize a range of therapeutic approaches, including medication management, psychotherapy, and lifestyle interventions, to help patients achieve better mental health outcomes.
What kind of education and training do psychologists undergo?
To become a licensed psychologist, individuals typically complete a doctoral degree in psychology, followed by supervised clinical training. Many psychologists focus on psychological treatment and are skilled in providing therapy to help clients manage their mental health challenges. In contrast, psychiatrists undergo a different path, including medical school and residency training in psychiatry. The differences between psychologists and psychiatrists lie primarily in their approaches; while psychologists often focus on psychological treatment, psychiatrists can diagnose and treat mental health issues using medications and medical interventions. This distinction highlights the career as a psychologist vs a psychiatrist, showcasing the varied roles within the field of mental health.
Both professionals play vital roles in the diagnosis and treatment of mental health disorders. Psychiatrists may work in hospitals, where they can provide comprehensive care, including medication management. On the other hand, many psychologists are affiliated with private practices or community organizations, facilitating therapy sessions that help clients improve their mental well-being. Understanding the similarities and differences between these professions is crucial for anyone considering a career in mental health, as it informs their educational and training choices in the world of psychology vs psychiatry.
How do the roles and salaries of psychiatrists and psychologists differ?
Psychiatrists typically earn higher salaries due to their medical training and ability to prescribe medication. They complete medical school and residency training, requiring 8+ years after college.
Psychologists generally complete 5-7 years of graduate training focused on therapeutic techniques and psychological assessment. They specialize in conducting therapy and psychological testing.